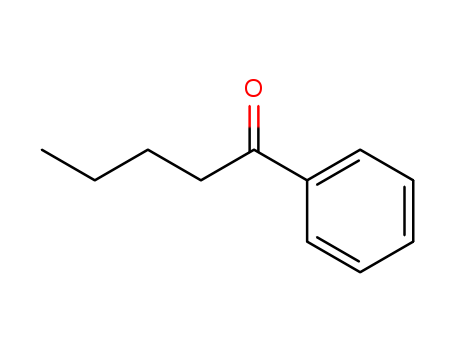
Valerophenone literature
Palladium on carbon-catalyzed Α-alkylation of ketones with alcohols as electrophiles: Scope and mechanism
Bennedsen, Niklas R.,Mortensen, Rasmus L.,Kramer, S?ren,Kegn?s, S?ren
, p. 153 - 160 (2019)
The α-alkylation of ketones with alcohols represents a green strategy for the formation of crucial carbon–carbon bonds since it only produces water as byproduct. In terms of reaction mechanism, the evidence for homogeneous catalysis supports a catalytic hydrogen-borrowing pathway; however, the reaction mechanism has not been investigated for heterogeneous Pd/C catalysts. Here, we report an improved method for α-alkylation of ketones with alcohols using commercially available Pd/C, ubiquitous in organic synthesis labs, as catalyst. The reaction conditions are mild compared to state-of-the-art for both homo- and heterogeneous catalysts, and the developed conditions produces quantitative yields for most ketones and alcohols. A hot filtration experiment and recycling of the catalyst supports the heterogeneous nature of catalysis. Importantly, the reaction mechanism is studied for the first time by a combination of stoichiometric experiments and kinetic analyses by in-situ IR (React-IR).
-
Gassman,P.G.,Richmond,G.D.
, p. 2355 - 2357 (1966)
-
-
Pittman,C.U.,Hanes,R.M.
, p. 1194 - 1197 (1977)
-
A simple synthesis of ketone from carboxylic acid using tosyl chloride as an activator
Jana, Samaresh,Sahoo, Debasis,Sarkar, Sohini
, (2019)
An effective process for the conversion of carboxylic acid to ketone has been discovered. In this process, carboxylic acid has been activated using p-toluene sulphonyl group. Under the optimized condition, aromatic, aliphatic heteroaromatic carboxylic acids have been proved to be good substrates for this methodology. The byproduct of this reaction can be removed very easily during work up process. Also, one equivalent of organometallic reagent is sufficient to complete this transformation.
Reaction of Lithium Dialkylcuprates with S-2-Pyridiyl Thioates in the Presence of Oxygen. A Carboxylic Ester Synthesis
Kim, Sunggak,Lee, Jae In,Chung, Bong Young
, p. 1231 - 1232 (1981)
Reaction of lithium dialkylcuprates with S-2-pyridyl thioates in the presence of oxygen affords carboxylic esters in high yields, whereas under nitrogen it affords ketones.
-
Granito,Schultz
, p. 879 (1963)
-
New Heterocuprates with Greatly Improved Thermal Stability
Bertz, Steven H.,Dabbagh, Gary,Villacorta, G. M.
, p. 5824 - 5826 (1982)
-
-
Lee,J.B.
, p. 5669 - 5672 (1966)
-
Ready Coupling of Acid Chlorides with Tetra-alkyl-lead Derivatives Catalysed by Palladium
Yamada, Jun-ichi,Yamamoto, Yoshinori
, p. 1302 - 1303 (1987)
Palladium-catalysed coupling of acid chlorides with tetra-alkyl-lead derivatives gives the corresponding ketones in high yields under mild conditions.
A FACILE PREPARATION OF TELLUROL ESTERS FROM PHENYLTELLUROTRIMETHYLSIANE AND ACYL CHLORIDES
Sasaki, Kazuaki,Aso, Yoshio,Otsubo, Tetsuo,Ogura, Fumio
, p. 977 - 978 (1986)
Phenyltellurotrimethylsilane cleanly reacted with acyl chloride, giving tellurol ester in an excellent yield.The high rectivity of tellurol ester toward lithium organocuprate was demonstrated.
Palladium-Catalyzed Cross-Coupling Reactions of Carboxylic Anhydrides with Organozinc Reagents
Wang, Donghui,Zhang, Zhaoguo
, p. 4645 - 4648 (2003)
(Matrix presented) Negishi-type cross-coupling reaction was effected by employing organozincs and anhydrides or mixed anhydrides that formed in situ from sodium salts of the corresponding acids and ethyl chloroformate under the catalysis of palladium(0). A general method for preparing symmetrical/ unsymmetrical ketones was developed.
A Palladium Bipyridyl Complex Grafted onto Nanosized MCM-41 as a Heterogeneous Catalyst for Negishi Coupling
Wu, Wei-Yi,Lin, Tze-Chiao,Takahashi, Tamotsu,Tsai, Fu-Yu,Mou, Chung-Yuan
, p. 1011 - 1019 (2013)
The Negishi coupling of aryl bromides or acyl chlorides with organozinc chlorides catalyzed by a palladium bipyridyl complex anchored on nanosized mobile crystalline material 41 (MCM-41) were investigated. The reactions proceeded smoothly with a very low catalyst loading in THF at 70°C for electron-deficient aryl bromides, which gave good to high yields of the Negishi coupling products. However, reactions in toluene at 110°C were required if electron-rich aryl bromides were employed. For acyl chlorides, the reactions could be performed in THF at 50°C and the corresponding ketones and ynones were obtained in high yields. After centrifugation, it was possible to easily recover the supported catalyst from the reaction mixture, and this could be reused several times without any retreatment or regeneration with only a slight decrease in activity.
ANWENDUNG NICHTSTABILISIERTER EISEN(II)-ALKYLE ALS HOCHSELEKTIVE NUCLEOPHILE ALKYLIERUNGSREAGENZIEN
Kauffmann, Thomas,Laarmann, Barbara,Menges, Detlef,Voss, Karl-Uwe,Wingbermuehle, Dorothea
, p. 507 - 510 (1990)
Nonstabilized Fe(II) alkyls (RFeCl, R2Fe, R3FeM, R4FeM2; R=Me, n-Bu, M=Li, MgBr) are readily accessible in solution (THF, Et2O, CH2Cl2) by reaction of MeLi, MeMgBr, n-BuLi or n-BuMgBr, respectively, with FeCl2 at -78 to -50 deg C.The needed FeCl2 can be made by in-situ-reduction with RLi or RMgBr.For checking the transmetallation process the "β-bromostyrene-ketone-test" is especially favorable in case of the methyl derivatives.The prepared Fe compounds are alkylating reagents of high selectivity.
O-Benzoylbenzoic acids by the reaction of lithium 2-lithiobenzoates with acid chlorides. A contribution to the chemistry of alizarin and podophyllotoxin
Parham,Bradsher,Edgar
, p. 1057 - 1061 (1981)
-
Nickel N-heterocyclic carbene-catalyzed cross-coupling reaction of aryl aldehydes with organozinc reagents to produce aryl ketones
Jin, Cheng,Gu, Lijun,Yuan, Minglong
, p. 4341 - 4345 (2015)
The transformation of aromatic aldehydes into aryl ketones by nickel-catalyzed cross-coupling has been developed. This transformation represents an efficient and attractive synthetic utilization of organozinc reagents. The reaction provides a mild, practical method toward the synthesis of aryl ketones which are versatile intermediates and building blocks in organic synthesis.
Polystyrene resins containing 1,3-propanedithiol functions for solid-phase organic syntheses
Bertini, Vincenzo,Pocci, Marco,Lucchesini, Francesco,Alfei, Silvana,De Munno, Angela
, p. 864 - 866 (2003)
A completely odourless reliable synthesis of styrenic resins containing 1,3-propanedithiol functions able to form 1,3-dithiane derivatives with carbonyl compounds and back up the chemistry of thioacetals and thioketals is reported. The degree of functionalisation of the resin can be easily determined through the composition of the copolymerising mixture and confirmed by titration. The resins show good accessibility to various reagents and are effective for solid-phase synthesis being exploitable in the field of combinatorial chemistry.
Alcohols for the α-alkylation of methyl ketones and indirect aza-wittig reaction promoted by nickel nanoparticles
Alonso, Francisco,Riente, Paola,Yus, Miguel
, p. 4908 - 4914 (2008)
Nickel nanoparticles have been found to activate primary alcohols used for the α-alkylation of ketones or in indirect aza-Wittig reactions. These processes involve hydrogen transfer from the alcohol to the intermediate α,β-unsaturated ketone or imine, respectively. All these reactions are carried out in the absence of any ligand, hydrogen acceptor or base under mild reaction conditions. For the first time nickel is employed as a potential alternative to noble-metal-based catalysts in both reactions. A reaction mechanism is proposed on the basis of some deuteration experiments. Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, 2008.
-
Hauser,Humphlett,Weiss
, p. 426 (1948)
-
Regioselective ring-opening of cyclopropyl ketones with organometallic reagents
Ichiyanagi, Tsuyoshi,Kuniyama, Satoru,Shimizu, Makoto,Fujisawa, Tamotsu
, p. 1149 - 1150 (1997)
Regioselective ring-opening reaction of cyclopropyl ketones was conducted successfully, in which the reaction of cyclopropyl phenyl ketone with trimethylaluminum catalyzed by nickel acetyl-acetonate gave the ring-opening product in up to 76% yield.
-
Kurts et al.
, p. P21 (1969)
-
Chemiluminescence of Imino-1,2-dioxetan Formed from Ketenimine and Singlet Oxygen
Ito, Yoshikatsu,Yokoya, Hiroaki,Kyono, Kazuaki,Yamamura, Soichiro,Yamada, Yutaka,Matsuura, Teruo
, p. 898 - 900 (1980)
The chemiluminescent properties of several imino-1,2-dioxetans prepared by the photosensitized oxygenation of ketenimines at -78 degC, indicate that the energy level of the transition state for their decomposition to the corresponding ketones and isocyanates is low and that the decomposition proceeds via a biradical mechanism.
A Novel Ru(VII)/Ru(IV) Mediatory System for Electrooxidation of Primary and Secondary Alcohols, Leading to Aldehydes and Ketones
Torii, Sigeru,Yoshida, Akihito
, p. 369 - 370 (1995)
A soluble Ru(VII)/Ru(IV) redox system in MeCN/H2O(9/1 v/v)-Bu4NOH-(Pt/Pt) was found to be a mild oxidizing method for the electrochemical conversion of primary and secondary alcohols into their corresponding aldehydes and ketones under basic conditions.
Suzuki-Miyaura coupling of simple ketones via activation of unstrained carbon-carbon bonds
Xia, Ying,Wang, Jianchun,Dong, Guangbin
, p. 5347 - 5351 (2018)
Here, we describe that simple ketones can be efficiently employed as electrophiles in Suzuki-Miyaura coupling reactions via catalytic activation of unstrained C-C bonds. A range of common ketones, such as cyclopentanones, acetophenones, acetone and 1-indanones, could be directly coupled with various arylboronates in high site-selectivity, which offers a distinct entry to more functionalized aromatic ketones. Preliminary mechanistic study suggests that the ketone α-C-C bond was cleaved via oxidative addition.
A New Oxidizing Reagent: Triethylsilyl Hydrotrioxide
Posner, Gary H.,Webb, Kevin S.,Nelson, William M.,Kishimoto, Takashi,Seliger, Howard H.
, p. 3252 - 3254 (1989)
Triethylsilyl hydrotrioxide (Et3SiOOOH) is a new, short-lived oxidizing agent that can react at -78 deg C directly and rapidly with olefins to form 1,2-dioxetanes and oxidatively cleaved carbonyl products.
Nickel catalyzed cross-coupling of modified alkyl and alkenyl Grignard reagents with aryl- and heteroaryl nitriles: Activation of the C-CN bond
Miller, Joseph A.,Dankwardt, John W.
, p. 1907 - 1910 (2003)
The nickel catalyzed cross-coupling of alkyl and alkenyl Grignard reagents with aryl nitrile derivatives affords good yields of the corresponding aryl alkanes or aryl alkenes via activation of the C-CN bond. To prevent direct addition of the nucleophile to the nitrile group, the reactivity of the Grignard reagent was modulated by reaction with either LiOt-Bu or PhSLi prior to cross-coupling. The optimum catalyst was determined to be NiCl2(PMe3)2, which is a convenient air stable commercially available complex.
Reactivities of mixed organozinc and mixed organocopper reagents. Part 13 Kinetic study for phosphine-catalyzed acylation of alkylarylzincs and effect of residual group on the transfer rate of alkyl group
?mür Pekel, ?zgen
, p. 190 - 195 (2016)
Kinetics of reactions of di-n-butylzinc, n-Bu2Zn, and mixed n-butyl(substituted phenyl)zinc reagents and n-Bu(functional group (FG)-C6H4)Zn with benzoyl chloride in the presence of tri-n-butylphosphine have been investigated. Reaction rates of transferable n-butyl group have been determined in tetrahydrofuran at 0 °C to compare the transfer rate of n-butyl group in homo and mixed diorganozincs. Rate law is consistent with a third-order reaction, which is first order in diorganozinc, benzoyl chloride, and n-Bu3P, and a mechanism was proposed. The lower reaction rate of n-BuPhZn than that of n-Bu2Zn and negative reaction constant in Hammett plot are in accordance with the carbanionic charge of transferable n-butyl group in the acylation reaction. These findings support the hypothesis that the reaction rate of transferable group, RT, changes depending upon the residual group, RR, in RRRTZn reagents.
A Palladium-Catalyzed Synthesis of Ketones from Acid Chlorides and Organozinc Compounds
Grey, Roger A.
, p. 2288 - 2289 (1984)
-
Selective copper-catalyzed coupling reactions of (α-acetoxyhexyl)tricyclohexyltin
Linderman, Russell J.,Siedlecki, James M.
, p. 6492 - 6493 (1996)
-
Oxidative Nucleophilic Addition of Organovanadium Reagents to Aldehydes with Formation of Ketones
Hirao, Toshikazu,Misu, Daisuke,Agawa, Toshio
, p. 7179 - 7181 (1985)
-
Direct and efficient one-pot preparation of ketones from aldehydes using N-tert-butylphenylsulfinimidoyl chloride
Crawford, James J.,Henderson, Kenneth W.,Kerr, William J.
, p. 5073 - 5076 (2006)
(Chemical Equation Presented) A general, one-pot process has been established to prepare ketones from aldehydes using N-tert- butylphenylsulfinimidoyl chloride. By employing the developed protocol, a range of unsymmetrical ketones has been prepared in good yields from aldehydes in one simple synthetic operation.
Nucleophilic properties of butyllithium versus free carboxylic acids
Einhorn,Einhorn,Luche
, p. 2771 - 2774 (1991)
In opposition to the generally accepted idea, butyl lithium is not only a deprotonating agent for free carboxylic acids, but can also act as a nucleophile on the carbon oxygen double bond.
Reactivities of mixed organozinc and mixed organocopper reagents, 2. Selective n-alkyl transfer in tri-n-butylphosphine-catalyzed acylation of n-alkyl phenylzincs; an atom economic synthesis of n-alkyl aryl ketones
Erdik, Ender,Pekel, ?zgen ?mür
, p. 1501 - 1503 (2009)
Tri-n-butylphosphine-catalyzed acylation of mixed n-alkyl phenylzincs with aromatic acyl halides in THF is efficient in selective transfer of n-alkyl groups to produce n-alkyl aryl ketones in good yields. This route provides an atom economic organocatalyzed alternative to transition metal-catalyzed acylation of di-n-alkylzincs.
H2-Generation from Alcohols by the MOF-Based Noble Metal-Free Photocatalyst Ni/CdS/TiO2@MIL-101
Tilgner, Dominic,Klarner, Mara,Hammon, Sebastian,Friedrich, Martin,Verch, Andreas,De Jonge, Niels,Kümmel, Stephan,Kempe, Rhett
, p. 842 - 847 (2019)
The synthesis of important classes of chemical compounds from alcohols helps to conserve Earth's fossil carbon resources, since alcohols can be obtained from indigestible and abundantly available biomass. The utilisation of visible light for the activation of alcohols permits alcohol-based C-N and C-C bond formation under mild conditions inaccessible with thermally operating hydrogen liberation catalysts. Herein, we report on a noble metal-free photocatalyst able to split alcohols into hydrogen and carbonyl compounds under inert gas atmosphere without the requirement of electron donors, additives, or aqueous reaction media. The reusable photocatalyst mediates C-N multiple bond formation using the oxidation of alcohols and subsequent coupling with amines. The photocatalyst consists of a CdS/TiO2 heterojunction decorated with co-catalytic Ni nanoparticles and is prepared on size-optimised colloidal metal-organic framework (MOF) crystallites.
Oxidative rearrangement of internal alkynes to give one-carbon-shorter ketones via manganese porphyrins catalysis
Sheng, Wen-Bing,Jiang, Qing,Luo, Wei-Ping,Guo, Can-Cheng
, p. 5691 - 5693 (2013)
Oxidative rearrangement of internal alkynes catalyzed by manganese(III) porphyrin is described, which opens a new access to one-carbon-shorter ketones using molecular oxygen. Under the standard conditions, a variety of alkynes including diarylalkynes and arylalkylalkynes rearranged smoothly to the corresponding ketones in high yields. Based upon experimental observations, a plausible reaction mechanism is proposed.
Synthesis of Functionalized Ketones from Acid Chlorides and Organolithiums by Extremely Fast Micromixing
Nagaki, Aiichiro,Sasatsuki, Kengo,Ishiuchi, Satoshi,Miuchi, Nobuyuki,Takumi, Masahiro,Yoshida, Jun-ichi
, p. 4946 - 4950 (2019)
Synthesis of ketones containing various functional groups from acid chlorides bearing electrophilic functional groups and functionalized organolithiums was achieved using a flow microreactor system. Extremely fast mixing is important for high chemoselectivity.
IRON CATALYZED CROSS-COUPLING REACTIONS OF ACYL CHLORIDES WITH GRIGNARD REAGENTS. A MILD, GENERAL, AND CONVENIENT SYNTHESIS OF ALIPHATIC AND AROMATIC KETONES.
Fiandanese, V.,Marchese, G.,Martina, V.,Ronzini, L.
, p. 4805 - 4808 (1984)
Acyl chlorides couple with Grignard reagents at room temperature in the presence of catalytic amounts of tris(acetylacetonate)iron(III), Fe(acac)3.The reaction is general with respect to both reactants and provides a very mild and convenient method for the synthesis of aliphatic and aromatic ketones.
Reactivities of mixed organozinc and mixed organocopper reagents: 1 - Solvent controlled organic group transfer from mixed diorganozincs
Erdik, Ender,Pekel, ?zgen ?mür
, p. 338 - 342 (2008)
The selectivity of organyl group transfer in the copper catalyzed benzoylation of n-butyl phenylzinc in THF depends on N-, O- or P-donor cosolvents and additives as well as copper salts and Lewis acids. In THF:NMP (3:1) and in THF:diglyme (2:1), n-butyl group/ phenyl group transfer ratio is 9:1 whereas only n-butyl group transfer is observed in THF:n-Bu3P (1 equiv.) and only phenyl group transfer is observed in THF:TMEDA (2:1).
Carbon-carbon bond formation via oxidative-addition processes of titanium(II) reagents with π-bonded organic substrates. Reactivity modifications by Lewis acids and Lewis bases Part 22. Organic chemistry of subvalent transition metal complexes
Eisch, John J.,Gitua, John N.,Otieno, Peter O.,Shi, Xian
, p. 229 - 238 (2001)
A series of titanium(II) derivatives, TiE2, was prepared by alkylative reduction of TiE4 by two equivalents of n-butyllithium in THF at -78 to 25°C (E = Cl, F, OBun, OPri and 0.5 NPh-CH2-CH2-NPh). The LiE by-product could usually be removed by THF evaporation and dissolution of the TiE2 into toluene. All such TiE2 derivatives were shown to effect the epimetallation and oligomerization of olefins, acetylenes and carbonyl derivatives in varying degrees. Particularly pertinent were the isolation and chemical reactions of titanium(II) isoproxide, the postulated intermediate in the Kulinkovich synthesis of cyclopropanols from ethyl Grignard reagents and organic esters, as well as an intermediate in many allied reactions developed by the Sato group. The findings of the present study corroborate completely the foregoing hypothesis that titanium(II) isopropoxide is the key intermediate in such novel reactions in organic synthesis. Furthermore, Ti(OPrl)2 can be prepared readily in a relatively pure state and has been found to react with 1-alkenes, alkynes and ketones by epimetallation at 25°C to form three-membered titanacycles, which can be utilized in organic synthesis. Finally, the ease with which such TiE2 derivatives epimetallate unsaturated organic substrates has been shown to be decreased by the steric demands of E and by the coordination of Lewis bases or donor solvent to the titanium(II) center. Lewis acids, on the other hand, greatly increase the rate of epimetallation by TiE2. A dramatic illustration of this effect is in the action of TiCl2·Me2AlCl on unsaturated hydrocarbons, wherein the polymerization of ethylene and of 1-alkene and the cyclotrimerization of alkynes are found to occur at room temperature.
-
Richey,H.G. et al.
, p. 2187 - 2190 (1971)
-
Catalytic and chemoselective oxidation of activated alcohols and direct conversion of diols to lactones with in situ-generated bis-IBX catalyst
Seth, Saona,Jhulki, Samik,Moorthy, Jarugu Narasimha
, p. 2445 - 2452 (2013)
The twisted 3,3′-diiodo-2,2′,6,6′-tetramethoxybiphenyl-4, 4′-dicarboxylic acid (DIDA) was designed and synthesized for the in situ generation of Bis-IBX and catalytic oxidations. The seemingly better solubility of the in situ-generated Bis-IBX and the attenuated reactivity arising from its unique structural features and methoxy substituents allowed the catalytic oxidation of activated alcohols selectively using DIDA/oxone. Chemoselective oxidations were demonstrated for substrates containing two different hydroxy groups. Furthermore, the unique reactivity of DIDA was demonstrated for sequential oxidation reactions of 1,4- and 1,6-diols to give lactones catalytically in respectable yields.
Preparation of ketones via the palladium-catalyzed cross-coupling of acid chlorides with trialkylboranes
Kabalka, George W.,Malladi, Rama R.,Tejedor, David,Kelley, Shane
, p. 999 - 1001 (2000)
Trialkylboranes react with acid chlorides in the presence of palladium to generate alkyl and aryl ketones in good yields. (C) 2000 Elsevier Science Ltd.
A remarkable effect of ionic liquids in transition-metal-free aerobic oxidation of benzylic alcohols
Oda, Yoshiro,Hirano, Koji,Satoh, Tetsuya,Kuwabata, Susumu,Miura, Masahiro
, p. 5392 - 5394 (2011)
The transition-metal-free aerobic oxidation of benzylic alcohols is uniquely accelerated by a 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate (BMI-PF6)/PhCF3 biphasic system and Cs2CO 3 to afford the corresponding ketones in good yields. The reaction system is also applicable to an oxidative cross-esterification of primary benzyl alcohols with a higher aliphatic alcohol.
Simple one pot synthesis of ketone from carboxylic acid using DCC as an activator
Mekonnen, Habtamu Gelaw,Jana, Samaresh
, p. 1382 - 1384 (2019)
Simple one pot procedure for the conversion of carboxylic acid to ketone is described. Various carboxylic acids were converted to the corresponding ketones in excellent manner in presence of N,N′-dicyclohexylcarbodiimide (DCC) and organometallic reagents. Aromatic, heteroaromatic and aliphatic acids were converted to the corresponding ketones smoothly under the optimum conditions using organolithium reagents. In this process, desired products have been isolated from the crude reaction mixtures in moderate yields during the purification process.
Ring Expansion and Contraction of a Two-Carbon Bridged Spiropentane
Wiberg, Kenneth B.,Snoonian, John R.
, p. 1390 - 1401 (1998)
The reactions of tricyclo[4.1.0.01,3]heptan-4-one (5) and two related systems with diazomethane and m-CPBA were examined in order to determine the relative reactivity and migratory aptitudes for the three compounds. The reactions of 5 with diazomethane and m-CPBA yielded new derivatives of the tricyclo[5.1.0.01,3]octane ring system that showed that migration of cyclopropylcarbinyl is favored over cyclopropyl migration in this system. Photolysis of 5-diazotricyclo[4.1.0.01,3]heptan-4-one (23) in methanol and dimethylamine did not lead to ring contraction to the tricyclo[3.1.0.01,3]hexane ring system, but an interesting product was derived from an unusual rearrangement process in the photolysis in dimethylamine. Matrix photolysis of 23 at 15 K gave a decrease in the diazo band at 2085 cm-1 and the appearance of a new band at 2117 cm-1, which is a normal position expected for a small-ring ketene such as cyclopropylketene. Thus, matrix photolysis appears to have yielded a derivative of the previously unknown tricyclo[3.1.0.01,3]hexane ring system. The lithium enolate of 5 was characterized by NMR spectroscopy at -80 °C and was found to rearrange to m-cresol at -65 °C. The geometries of the bridged spiropentanes of this work were optimized at the MP2(frozen core)/6-31G* level of theory, and group equivalent values were derived in order to calculate the heats of formation for these compounds using the calculated energies.
Palladium-catalyzed carboacylation of alkenes by using acylchromates as acyl donors
Yamane, Motoki,Kubota, Yuko,Narasaka, Koichi
, p. 331 - 340 (2005)
Palladium-catalyzed arylacylation of alkenes proceeds by employing acylchromates as acyl donors. When active alkenes such as norbornene and methoxyallene are treated with an aryl iodide, an acylchromate, and a catalytic amount of Pd(OAc)2/2P(o-Tol)3, arylacylation of these alkenes proceeds at room temperature. From aryl iodides having an intramolecular alkene moiety, cyclization-acylation products are obtained via intramolecular arylpalladation followed by acylation with acylchromates.
-
Buchanan,Davis
, p. 1340 (1967)
-
Crystal structures and photoreactivity of transand cis-valerophenone diperoxides
Takahashi, Hiroki,Ito, Yoshikatsu
, p. 441 - 449 (2012)
The crystal structures of valerophenone diperoxides trans-1 and cis-1 were elucidated by X-ray crystallographic analysis. The 1,2,4,5-tetraoxane rings of both compounds adopt chair conformations. Intermolecular CH...O hydrogen bond, π-π, and CH/π interactions exist in cis-1, whereas only CH/π interactions exist in trans-1. In the asymmetric unit of the crystal, a half molecule exists for trans-1, while one molecule for cis-1 which shows wholemolecule disorder. Solid-state photolysis (at 254 nm) or solution-state thermolysis (at 150 °C) of trans-1 and cis-1 produced valerophenone (2) and butyl benzoate (3). Rationalization of the solid-state photoreactivity of the diperoxides by their crystal structures was attempted. Springer Science+Business Media, LLC 2011.
A new method for the synthesis of ketones: The palladium-catalyzed cross-coupling of acid chlorides with arylboronic acids
Haddach, Mustapha,McCarthy, James R.
, p. 3109 - 3112 (1999)
The cross-coupling reaction of acid chlorides with arylboronic acids, using catalytic amounts of Pd(PPh3)4 and five equivalents Cs2CO3, under anhydrous conditions provides a new method for the synthesis of ketones in good to moderate yields.
Nickel-Catalyzed Reductive Acylation of Carboxylic Acids with Alkyl Halides and N-Hydroxyphthalimide Esters Enabled by Electrochemical Process
Guo, Lin,Xia, Raymond Yang,Xia, Wujiong,Yang, Chao,Zhang, Haoxiang,Zhou, Xiao
supporting information, (2022/03/31)
A sustainable Ni-catalyzed reductive acylation reaction of carboxylic acids via an electrochemical pathway is presented, affording a variety of ketones as major products. The reaction proceeds at ambient temperature using unactivated alkyl halides and N-hydroxyphthalimide (NHP) esters as coupling partners, which exhibits several synthetic advantages, including mild conditions and convenience of amplification (58% yield for 6 mmol scale reaction). (Figure presented.).
Selective Activation of Unstrained C(O)-C Bond in Ketone Suzuki-Miyaura Coupling Reaction Enabled by Hydride-Transfer Strategy
Zhong, Jing,Zhou, Wuxin,Yan, Xufei,Xia, Ying,Xiang, Haifeng,Zhou, Xiangge
supporting information, p. 1372 - 1377 (2022/02/23)
A Rh(I)-catalyzed ketone Suzuki-Miyaura coupling reaction of benzylacetone with arylboronic acid is developed. Selective C(O)-C bond activation, which employs aminopyridine as a temporary directing group and ethyl vinyl ketone as a hydride acceptor, occurs on the alkyl chain containing a β-position hydrogen. A series of acetophenone products were obtained in yields up to 75%.
Contra-Thermodynamic Positional Isomerization of Olefins
Zhao, Kuo,Knowles, Robert R.
supporting information, p. 137 - 144 (2022/01/19)
A light-driven method for the contra-thermodynamic positional isomerization of olefins is described. In this work, stepwise PCET activation of a more substituted and more thermodynamically stable olefin substrate is mediated by an excited-state oxidant an
Ruthenium-on-Carbon-Catalyzed Facile Solvent-Free Oxidation of Alcohols: Efficient Progress under Solid-Solid (Liquid)-Gas Conditions
Park, Kwihwan,Jiang, Jing,Yamada, Tsuyoshi,Sajiki, Hironao
, p. 1200 - 1205 (2021/12/29)
A protocol for the ruthenium-on-carbon (Ru/C)-catalyzed solvent-free oxidation of alcohols, which proceeds efficiently under solid-solid (liquid)-gas conditions, was developed. Various primary and secondary alcohols were transformed to corresponding aldehydes and ketones in moderate to excellent isolated yields by simply stirring in the presence of 10% Ru/C under air or oxygen conditions. The solvent-free oxidation reactions proceeded efficiently regardless of the solid or liquid state of the substrates and reagents and could be applied to gram-scale synthesis without loss of the reaction efficiency. Furthermore, the catalytic activity of Ru/C was maintained after five reuse cycles.