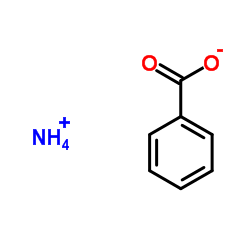
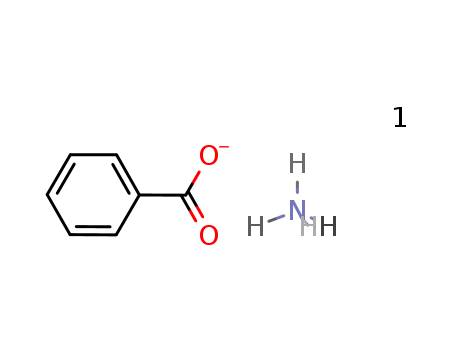
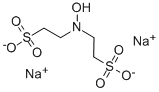
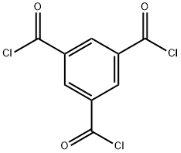
Ammonium benzoate literature
Green synthesis method of aromatic acid
-
Paragraph 0019-0020; 0022-0023; 0029-0030; 0032-0033, (2020/01/03)
The invention relates to a synthesis method of organic acid, in particular to a green synthesis method of aromatic acid, and belongs to the field of organic synthesis. According to the green synthesismethod of the aromatic acid, an aromatic cyano compound is used as a substrate, a corresponding aromatic acid ammonium salt is obtained after catalytic hydrolysis under catalysis of an alkali catalyst, the obtained aromatic acid ammonium salt is hydrolyzed to obtain the aromatic acid, at the same time, byproduct ammonia water is produced, and the alkali catalyst can be repeatedly applied for manytimes; and the structural formula of the aromatic cyano compound is as follows (please see the specification for the formula). The green synthesis method has the characteristics of simple operation,high product yield, easy separation and basically no generation of salt containing wastewater, small generation amount of wastewater, environmental friendliness and the like, in addition, the catalystcan further be reused for many times, and after repeated application of the catalyst, the total yield of a product can be close to 100%.
Synthesis, characterization, and thermodynamic study of ammonium benzoate C7H5O2NH4(s)
Yang, Wei-Wei,Di, You-Ying,Kong, Yu-Xia,Guo, Xiao-Yang,Tan, Zhi-Cheng
experimental part, p. 14 - 19 (2010/07/09)
Benzoic acid and concentrated ammonia were chosen as reactants and a novel compound (ammonium benzoate) was synthesized using the method of liquid phase reaction. FTIR, elemental analysis and X-ray powder diffraction technique were applied to characterize the structure and composition of the compound. Low-temperature heat capacities of the solid compound were measured by a precision automated adiabatic calorimeter over the temperature range from 80 to 399 K. A polynomial equation of the heat capacities was fitted by the least-squares method. In accordance with Hess' law, a thermochemical cycle was designed, the enthalpy change of the reaction of benzoic acid with ammonium acetate was determined as Δr Hm ° = (15.59 ± 0.50) kJ mo l- 1, and the standard molar enthalpy of formation of the compound was calculated as Δf Hm ° [ C7 H5 O2 N H4,s ] = - (472.65 ± 0.62) kJ mo l- 1 by an isoperibol solution-reaction calorimeter.
Process for preparing nitriles and isonitriles by dehydration reactions with propanephosphonic anhydrides
-
, (2008/06/13)
The invention concerns a method for producing: a) nitriles of formula (II) and b) isonitriles of formula (III) by reacting: a) carboxylic acid amides (RCO—NH2), ammonium salts of carboxylic acids (RCOO—NH4+) or carboxylic acids in the presence of ammonia or ammonium salts (RCOOH+NH3, RCOOH+NH4+) or b) formamides (H—CO—NHR) or mixtures of amines with formic acid, with cyclic phosphonic acid anhydrides while eliminating water at a temperature ranging from ?30 to +120° C., in which R represents an arbitrarily substituted linear or branched C1-C8 alkyl radical, a C3-C10 cycloalkyl radical, alkenyl radical, alkynyl radical or an aryl radical or heteroaryl radical. As a cyclic phosphonic acid anhydride, a 2,4,6,-substituted 1,3,5,2,4,6 -trioxatriphosphinane-2,4,6-trioxide of formula (I) is advantageously used, in which: x=3, 4 or 5; R′, independent of one another, represents open-chain or branched, saturated or unsaturated, straight-chain C1to C16 alkyl radicals or cyclic C3 to C16 alkyl radicals or aryl or heteroaryl.
AMMONOLYSIS OF PENTA-O-BENZOYL-α-D-GLUCOPYRANOSE IN AN APROTIC MEDIUM. CHARACTERIZATION OF THE PRODUCTS ISOLATED, AND CONFORMATIONAL ANALYSIS OF ELEVEN N-BENZOYL-D-GLUCOFURANOSYLAMINE DERIVATIVES
Salinas, Amelia E.,Sproviero, Jorge F.,Deulofeu, Venancio
, p. 71 - 99 (2007/10/02)
The reaction of penta-O-benzoyl-α-D-glucopyranose with chloroform-1,4-dioxane-liquid ammonia gave 1,1-bis(benzamido)-6-O-benzoyl-1-deoxy-D-glucitol (29.0percent), three partially benzoylated derivatives of N-benzoyl-α-D-glucofuranosylamine (23.6percent), a small proportion of N-benzoyl-di-O-benzoyl-β-D-glucofuranosylamine (0.2percent), and four partially benzoylated derivatives of α-D-glucopyranose (9.9percent).The structures of the hitherto-unknown products, and their anomeric configurations, were established by chemical and spectroscopic methods.The conformations in solution of both anomers of N-benzoyl-D-glucofuranosylamine, their partially benzoylated derivatives isolated from the ammonolysis reaction, and the per-O-acetyl derivatives of the various compounds were analyzed by (1)H-n.m.r.spectroscopy.