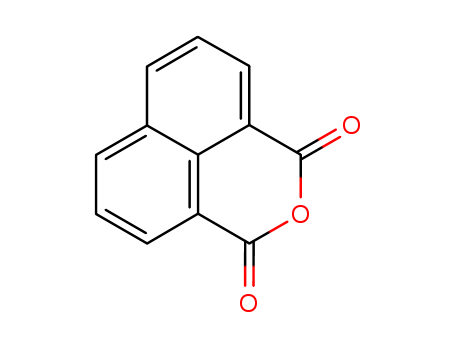
1,8-Naphthalic anhydride literature
Mechanistically optimized intramolecular catalysis in the hydrolysis of esters. Global changes involved in molecular reactivity
Yunes, Santiago F.,Gesser, Jose C.,Chaimovich, Hernan,Nome, Faruk
, p. 461 - 465 (1997)
The hydrolysis of the 2′,2′,2′-trifluoroethyl monoester of 1,8-naphthalic acid (1) proceeds via the monoanion with the intermediate formation of the corresponding anhydride. The rate constant for the formation of 1,8-naphthalic anhydride (2) is ca 2500 times faster than its rate of hydrolysis. The isotope effect in the plateau region and theoretical calculations at the PM3 level suggest that elimination of the alkoxide is the rate-limiting step for the reaction. Accordingly, decomposition of the isopropyl monoester of naphthalic acid proceeds 104 times slower than the spontaneous decomposition of 1. The remarkably high rate of monoester decomposition derives from the special configuration of the substrates and important contributions that arise from relief of torsional strain, which clearly includes electron redistribution due to the decrease in steric hindrance to resonance and the fact that proximity obviates solvation.
Reactions of hydroxyl radicals and ozone with acenaphthene and acenaphthylene
Reisen, Fabienne,Arey, Janet
, p. 4302 - 4311 (2002)
Acenaphthene and acenaphthylene are polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) emitted into the atmosphere from a variety of incomplete combustion sources such as diesel exhaust. Both PAHs are present in the gas phase under typical atmospheric conditions and
Degradation of acenaphthylene and anthracene by chemically modified laccase from Trametes versicolor
Liu, Yulong,Hua, Xiufu
, p. 31120 - 31122 (2014)
We are studying the chemically modified laccase from Trametes versicolor for use in the in vitro oxidation of two polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs), acenaphthylene and anthracene, in combination with 2,2′-azino-bis- (3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic acid) (ABTS) as a redox mediator. The results indicate that the maleic anhydride modified laccase (MA-Lac) improved the stability of laccase to temperature, pH and storage time compared with the free enzyme. After incubation for 72 h, the MA-Lac-ABTS system oxidized acenaphthylene and anthracene to more than 70% from the reaction mixture. This journal is the Partner Organisations 2014.
-
Koo,Schuster
, p. 847,850 (1979)
-
Photochemical Wolf Rearrangement of a Triplet Groung-State Carbene
Hayes, Richard A.,Hess, Thomas C.,McMahon, Robert J.,Chapman, Orville L.
, p. 7786 - 7787 (1983)
-
Naphthalimide-polyamine conjugate as well as preparation method and application thereof
-
Paragraph 0030; 0108-0110; 0112, (2021/02/10)
The invention discloses a naphthalimide-polyamine conjugate, which has a structural general formula as shown in I, a novel skeleton, high efficiency, low toxicity and good inhibitory activity for tumor cells. The invention also discloses a preparation method of the conjugate. Firstly, 3-amino groups with toxic and side effects of amonafide are removed, a phenylpyrazole structure fragment is introduced to the naphthalimide parent naphthalene ring, and a naphthalimide side chain with a polyamine chain is modified, acetyltransferase in vivo is prevented from acetylating the amino groups on the naphthalene ring of amonafideand, and toxic and side effects are reduced; and further by introducing a low-toxicity phenyl pyrazole active structure fragment, the naphthalimide polyamine conjugate witha novel skeleton, high efficiency and low toxicity is synthesized; and secondly, quinazoline with low toxicity is introduced to replace hydrogen atoms of amonafide 3-amino, so that the naphthalimide polyamine conjugate with anti-tumor activity and low toxicity is obtained. The invention also discloses an application of the conjugate in preparation of antitumor drugs, and good development potentialis realized.
A Pt(IV)-based mononitro-naphthalimide conjugate with minimized side-effects targeting DNA damage response via a dual-DNA-damage approach to overcome cisplatin resistance
Li, Linrong,Li, Yingguang,Liu, Hanfang,Ma, Jing,Niu, Jie,Xie, Songqiang,Yue, Kexin
, (2020/07/03)
Platinum(Pt)(II) drugs and new Pt(IV) agents behave the dysregulation of apoptosis as the result of DNA damage repair and thus, are less effective in the treatment of resistant tumors. Herein, mononitro-naphthalimide Pt(IV) complex 10b with minimized side-effects was reported targeting DNA damage response via a dual-DNA-damage approach to overcome cisplatin resistance. 10b displayed remarkably evaluated antitumor (70.10percent) activities in vivo compared to that of cisplatin (52.88percent). The highest fold increase (FI) (5.08) for A549cisR cells and the lowest (0.72) for A549 indicated 10b preferentially accumulated in resistant cell lines. The possible molecular mechanism indicates that 10b targets resistant cells in a totally different way from the existing Pt drugs. The cell accumulation and the Pt levels in genomic DNA from 10b is almost 5 folds higher than that of cisplatin and oxaliplatin, indicating the naphthalimide moiety in 10b exhibits preferentially DNA damage. Using 5′-dGMP as a DNA model, the DNA-binding properties of 10b (1 mM) with 5′-dGMP (3 mM) in the presence of ascorbic acid (5 mM) deduced that 10b was generated by the combination of cisplatin with 5′-dGMP after reduction by ascorbic acid. Moreover, 10b promoted the expression of p53 gene and protein more effectively than cisplatin, leading to the increased anticancer activity. The up-regulated γH2A.X and down-regulated RAD51 indicates that 10b not only induced severe DNA damage but also inhibited the DNA damage repair, thus resulting in its higher cytotoxicity in comparison to that of cisplatin. Their preferential accumulation in cancer cells (SMMC-7721) compared to the matched normal cells (HL-7702 cells) demonstrated that they were potentially safe for clinical therapeutic use. In addition, the higher therapeutic indices of 10b for 4T1 cells in vivo indicated that naphthalimide-Pt(IV) conjugates behaved a vital function in the treatment of breast cancer. For the first time, our study implies a significant strategy for Pt drugs to treat resistance cancer targeting DNA damage repair via dual DNA damage mechanism in a totally new field.
Tetravalent platinum naphthalimide complex, preparation method and application thereof
-
Paragraph 0079; 0092-0095; 0099-0102; 0106-0109; 0113-0116, (2020/07/21)
The invention belongs to the technical field of medicinal chemistry, and particularly relates to a tetravalent platinum naphthalimide complex, a preparation method and application thereof. The tetravalent platinum naphthalimide complex has good anti-tumor activity, which is better than that of cis-platinum and oxaliplatin, and the tetravalent platinum naphthalimide complex has better stability than bivalent platinum like cis-platinum, carboplatin and oxaliplatin. According to the invention, the naphthalimide modified tetravalent platinum has good targeting performance on tumor cells, high selectivity on tumor cells is improved, and different from a classic divalent platinum drug, the complex provided by the invention regulates and controls subcellular organelles and cell nucleus functionsto reverse drug resistance by targeting a tumor high polyamine microenvironment, and relieves immunosuppression of T cells around tumors at the same time. The complex provided by the invention also solves the problems of poor solubility, tedious clinical compatibility, poor patient immunity in clinical application of chemotherapeutic drugs and the like of previous bivalent platinum antitumor drugs, and has good fat solubility and water solubility.
A 3, 9 - perylene dicarboxylic acid preparation method
-
Paragraph 0018; 0019; 0020, (2019/03/23)
The invention discloses a 3, 9 - perylene dicarboxylic acid of preparation method, specific step is ice-acetic acid in a solvent, in the dihydro e is obtained under the action of the sodium dichromate of 1, 8 - naphthalenedicarboxylic anhydride; 1, 8 - naphthalenedicarboxylic anhydride in saturated ammonia under the action of the acylation to obtain the 1, 8 - naphthalene asia amide; 1, 8 - naphthalene asia amide in potassium hydroxide and anhydrous sodium acetate manufacturing of the alkaline environment in the alkaline environment in C - C under high-temperature conditions obtained by coupling the 3, 4, 9, 10 - perylenetetracarboxylic acid diimide; 3, 4, 9, 10 - perylenetetracarboxylic acid diimide in under the action of the strong acid is converted into the 3, 4, 9, 10 - [...]; 3, 4, 9, 10 - [...] in microwave reactor in alkaline hydrolysis by the decarboxylation of 3, 9 - perylene dicarboxylic acid. The invention synthetic process more economic, environmental protection, high-efficient and simple.