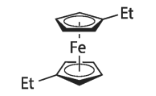
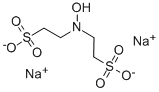
1,1'-DIETHYLFERROCENE literature
Stereo- and enantioselectivity in catalytic hydrogenolysis of chiral substituted ferrocenes to give cyclopentanes
Sokolov, V. I.,Troitskaya, L. L.,Khrushcheva, N. S.,Reutov, O. A.
, p. 227 - 234 (1989)
The catalytic hydrogenolysis of 1,2-disubstituted ferrocenes having planar chirality and functional groups such as carboxyl (including ester) or tertiary amino proceeds under mild conditions (1 atm of H2, Pd/C, CF3COOH, 50 deg C) with the retention of fun
Thermodynamics and molecular dynamics of some ferrocene derivatives
Domracheva,Karyakin,Sheiman,Kamelova,Larina,Suvorova,Domrachev
, p. 1647 - 1655 (1999)
The heat capacities of acetylferrocene, 1,1′-diacetylferrocene, and 1,1′-diethylferrocene were investigated by low-temperature adiabatic calorimetry in the temperature range from 5 to 300 K and their thermodynamic functions were calculated. The enthalpies
The reactions of acylferrocenes with samarium diiodide: Reduction, deoxygenation, reductive coupling and rearrangement
Jong, Shean-Jeng,Fang, Jim-Min,Lin, Chun-Hsu
, p. 42 - 45 (1999)
Acylferrocenes reacted with samarium diiodide in the presence of water to give the corresponding (α-hydroxyalkyl)ferrocenes or alkylferrocenes depending on the reaction time and temperature. On treatment with samarium diiodide in the absence of water, ferrocenecarbaldehyde underwent a reductive coupling to give pinacols, whereas acetylferrocene yielded 3,3-diferrocenyl-2-butanone and 2,3-diferrocenyl-2-butene via the subsequent rearrangement and deoxygenation.
Simple reduction of ferrocenyl aldehydes and ketones by sodium boranuide in trifluoroacetic acid: New, efficient, general preparation of alkylferrocenes
Bhattacharyya, Sukanta
, p. 1381 - 1383 (1996)
Alkylferrocenes are obtained in excellent yields by ionic hydrogenation of ferrocenyl aldehydes and ketones using sodium boranuide and trifluoroacetic acid.
Ionic hydrogenation of acylferrocenes using zinc borohydride: An efficient, mild method for the preparation of alkylferrocenes
Bhattacharyya, Sukanta
, p. 1065 - 1066 (1996)
An effective mild procedure for the reductive deoxygenation of α-ferrocenyl aldehydes, ketones, and alcohols into the corresponding alkylferrocenes is described using a combination of zinc borohydride and zinc chloride. This is the first example of such reactivity of zinc borohydride. The present method allows the synthesis of alkylferrocenes bearing terminally functionalized pendant chains.
Redox-active binary eutectics: Preparation and their electrochemical properties
Chen, Hui,Niu, Zhihui,Zhao, Yu
, (2021/04/19)
Eutectics are emerging as promising candidate for electrochemical energy storage. However, the eutectics usually show high viscosity that usually arises from strong intermolecular interactions greatly limits their application. In this communication, we design and prepare two redox-active molecules that both are able to form binary eutectics with TBMA-TFSI. Combined experimental and computational studies indicate the intermolecular interaction is weakened after eutectic formation, resulting in decreased viscosity and enhanced ionization ratio of TBMA-TFSI without affecting the redox behaviors of the individual molecules. Further, the redox-active binary eutectic is used as solvent-free electrolyte for battery application.
Preparation method of diethylferroene with purity being greater than 99%
-
Paragraph 0037; 0038; 0039, (2019/12/25)
The invention relates to a preparation method of diethylferroene with purity being greater than 99%. The preparation method comprises the steps that high-content diacetylferrocene crude products are synthesized through an acylation technology firstly; a recrystallization and column separation series-connection method is utilized to separate the synthesized crude products, and thus high-content diacetylferrocene intermediates are obtained; and then the intermediates are reduced through a reduction catalyst and separated and purified, and thus the high-purity diethylferroene is obtained. The preparation method has the beneficial effects that 1, the purity of the intermediate diacetylferrocene with the large polarity difference is increased to be greater than 99% through a chromatographic column purification method, and the fact is the key for obtaining the high-purity target product; and 2, a high-purity borane-methyl sulfide complex with the extremely-high catalytic efficiency is selected, compared with an amalgam reduction method, the synthesis condition is mild, post-treatment is easy, and environmental protection is achieved.
Ferrocenyl-based redox-reversible surfactant and preparation method of thereof
-
Paragraph 0020; 0022, (2018/01/19)
The invention provides a ferrocenyl-based redox-reversible surfactant and a preparation method thereof, and relates to the field of redox switch type surfactants. The ferrocenyl-based redox-reversible surfactant is prepared from a precursor compound ferrocene, acetyl chloride, zinc amalgam, bromoundecanoic acid, thionyl chloride and trimethylamine as raw materials. The synthesized surfactant molecules are easy to prepare, the yield of the intermediate diacetylferrocene is effectively improved, a new feeding sequence is provided, and the problem of reduction of ferrocene due to oxidation reaction is effectively solved. The surfactant can be used as an electrode surface modification material for glucose detection.
One-pot synthesis of 1,1′-bis(2-amino)ethyl-substituted ferrocenes from the reaction of spiro[2.4]hepta-4,6-diene with lithium amides: An expedient route into functionalized ferrocenophanes
Joly, Kevin M.,Kariuki, Benson M.,Coe, Diane M.,Cox, Liam R.
, p. 358 - 366 (2008/10/09)
The reaction of lithium amides with spiro[2.4]hepta-4,6-diene 2 affords the corresponding (2-aminoethyl)CpLi cyclopropane-ring-opened product that can be trapped in situ with FeCl2 to provide a direct route into 1,1′-bis-aminoethyl ferrocenes 3. In addition to the desired bis-amine products, a number of interesting ferrocene byproducts have been identified. Their formation can be attributed to the associated Bronsted basicity of the lithium amide nucleophiles and their ability to participate in SET processes, opening-up alternative reaction pathways. The desired aminoethyl-substituted ferrocene products are derived primarily from direct nucleophilic cyclopropane ring-opening rather than via amidolithiation of vinylCp intermediates.