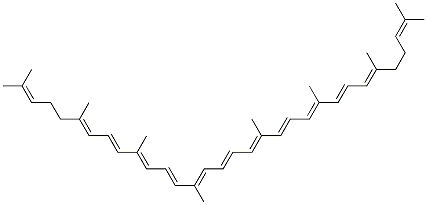
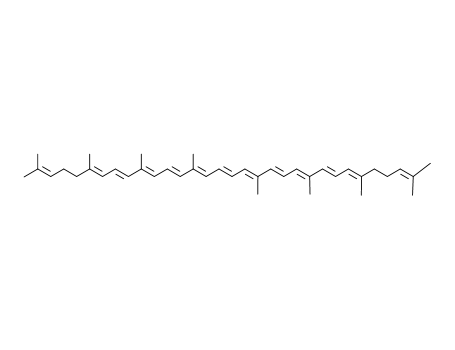
Lycopene literature
Practical Synthesis of Lycopene
Song, Xiaohua,Xu, Huiting,Ye, Weidong,Lv, Chunlei,Cao, Ruiwei,Wu, Chunlei,Shen, Runpu
, p. 350 - 354 (2016)
-
A novel and practical synthetic route for the total synthesis of lycopene
Shen, Runpu,Jiang, Xiaoyue,Ye, Weidong,Song, Xiaohua,Liu, Luo,Lao, Xuejun,Wu, Chunlei
, p. 5610 - 5614 (2011)
A novel route for the total synthesis of lycopene 1 is described. The synthesis is based on: (i) a condensation between 4,4-dimethoxy-3-methylbutanal 4 and methylenebisphosphonic acid tetraethyl ester 5, leading to the C6-phosphonate 6, followed by (ii) a modified Wittig-Horner reaction between 6 and 6-methyl-5-hepten-2-one 7 producing dimethoxy-3,5,9-triene 8, and (iii) another modified Wittig-Horner reaction between C15-phosphonate 2 and C10-triene dialdehyde 3 producing all-E-lycopene. The synthetic steps are easily operated and practical for the large-scale production.
Kinetic studies of lycopene isomerization in a tributyrin model system at gastric pH
Moraru, Catalin,Lee, Tung-Ching
, p. 8997 - 9004 (2005)
A semi-preparative HPLC method was developed in order to isolate and purify the 13-cis-lycopene isomer in tomato-based materials. The result was compared with the naturally predominant all-trans-lycopene isomer, in terms of stability to gastric pH at physiological temperature in a tributyrin model system. Kinetic experiments confirmed that lycopene isomerization is a reversible reaction, and under these conditions the all-trans isomer is more stable than the 13-cis isomer. In addition, it was found that at gastric pH 13-cis-lycopene would predominantly isomerize to the all-trans form rather than undergo oxidation/breakdown. A simulation based on the rate constants calculated in the kinetic study indicated that at gastric pH the lycopene isomeric distribution aimed toward an equilibrium characterized by approx 16% 13-cis-, 16% 9-cis-, and 68% all-trans-lycopene. This study suggests that pH-driven isomerization in the stomach is at least partially responsible for the relatively high cis-lycopene proportion found in vivo.
Method for preparing lycopene
-
Paragraph 0047-0051; 0053-0056; 0058-0061, (2017/12/30)
The invention discloses a method for preparing lycopene. According to the method, a target product, i.e., the lycopene can be obtained through subjecting 3,7-dimethyl-1,6-octadiene-diethyl phosphate and 2,6,11,15-tetramethyl-2,4,6,8,10,12,14-hexadeca-carbon heptaene dialdehyde, which serve as raw materials, to two step reactions, i.e., a rearrangement dissociation reaction and a condensation reaction only. According to the method, the trans-form content is high, isomerization is not required to be carried out, the route is simple, the operation is simple, the source of the raw materials is convenient, the cost is low, and the recovery rate is high, so that the method is applicable to large-batch industrial production.
Method for preparing lycopene
-
Paragraph 0042-0045, (2017/05/03)
The invention provides a method for preparing lycopene. The method comprises the following steps: under alkaline condition, pseudoionone and methyl chloroacetate are subjected to a reaction to obtain epoxide, then the epoxide is subjected to hydrolysis and decarboxylation under acidic condition to obtain 2,6,10-trimethyl-3,5,9-undecatriene-1-aldehyde; 2,6,10-trimethyl-3,5,9-undecatriene-1-aldehyde and tetraethyl methylenediphosphonate are subjected to a condensation reaction to obtain 3,7,11-trimethyl-1,4,6,10-tetraene dodecyl dialkyl phosphate; 3,7,11-trimethyl-1,4,6,10-tetraene dodecyl dialkyl phosphate is subjected to transposition, and then is subjected to a Wittig-Horner condensation reaction with 2,7-dimethyl-2,4,6-dimethyl-1,8-dialdehyde to obtain lycopene. The preparation method has the advantages of easy acquisition of the raw materials, short synthesis route, and low cost, and is suitable for industrial production.
METHODS FOR PREPARATION OF LYCOPENES FROM C15-WITTIG SALTS AND METHODS FOR PURIFICATION OF HIGH ALL-E CONTAINING AND HIGH 6Z CONTAINING C15-WITTIG SALTS
-
Paragraph 0027, (2016/02/10)
The present invention relates to methods for preparation of lycopenes, especially to lycopenes with high all-E contents or high 6Z contents from C15-Wittig slats mixtures. (with high all-E-contents and high 6Z-contents, respectively). C15-Wittig slats mixtures are purified and 6Z-C15-Wittig salts are extracted from the mixtures. The extracted 6Z-C15-Wittig salts are, used in the synthesis of lycopenes with high 6Z contents and the residues are used in the synthesis of lycopenes with high All-E contents.