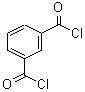
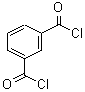
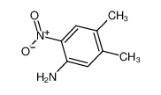
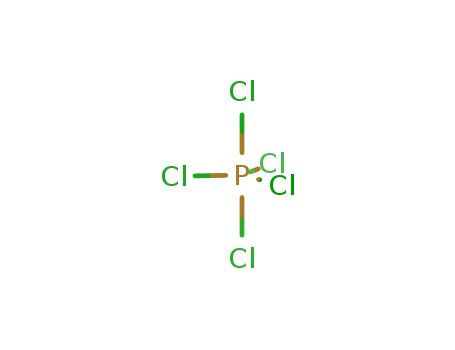1,3-Benzenedicarbonyl chloride literature
G4 Sensing Pyridyl-Thiazole Polyamide Represses c-KIT Expression in Leukemia Cells
Paul, Raj,Dutta, Debasish,Das, Tania,Debnath, Manish,Dash, Jyotirmayee
, p. 8590 - 8599 (2021)
Specific sensing and functional tuning of nucleic acid secondary structures remain less explored to date. Herein, we report a thiazole polyamide TPW that binds specifically to c-KIT1 G-quadruplex (G4) with sub-micromolar affinity and ~1 : 1 stoichiometry and represses c-KIT proto-oncogene expression. TPW shows up to 10-fold increase in fluorescence upon binding with c-KIT1 G4, but shows weak or no quantifiable binding to other G4s and ds26 DNA. TPW can increase the number of G4-specific antibody (BG4) foci and mark G4 structures in cancer cells. Cell-based assays reveal that TPW can efficiently repress c-KIT expression in leukemia cells via a G4-dependent process. Thus, the polyamide can serve as a promising probe for G-quadruplex recognition with the ability to specifically alter c-KIT oncogene expression.
Anion binding and fluoride ion induced conformational changes in bisurea receptors
Shu, Xi,Fan, Yu,Li, Shoujian,Jin, Yongdong,Xia, Chuanqin,Huang, Chao
, p. 2033 - 2045 (2020)
Two types of bisurea receptors, containing either 2,6-substituted phenyl or 2,6-substituted pyridine, are prepared, and their anion binding properties are investigated. Compared with the phenyl bisurea receptors, the pyridine bisurea receptors can be more easily converted to a cis-cis conformation from a trans-trans conformation, providing a cavity that more closely matches the volume of a fluoride ion and increasing the number of NH sites bound to the fluoride ion. As a result, the pyridine bisurea in cis-cis conformation shows stronger affinity and higher selectivity to fluoride ions, which is supported by crystal structure analysis and NMR titration experiments. Through DFT calculations, a mechanism of fluoride ion induced conformational changes of pyridine bisurea receptors is proposed, and the energy barriers of conformational changes for both types of receptors are determined.
Br?nsted acid-catalyzed chlorination of aromatic carboxylic acids
Yu, Zhiqun,Yao, Hongmiao,Xu, Qilin,Liu, Jiming,Le, Xingmao,Ren, Minna
supporting information, p. 685 - 689 (2021/04/09)
The chlorination of aromatic carboxylic acids with SOCl2 has been effectively performed by reacting with a Br?nsted acid as the catalyst. Based on this discovery, an efficient catalytic method that is cheaper than traditional catalytic methods was developed. 20 substrates were chlorinated offering excellent yields in a short reaction time. And the SOCl2/Br?nsted acid system has been used in a larger scale preparative reaction. A dual activation mechanism was proposed to prove the irreplaceable system of SOCl2/Br?nsted acid.
Method for increasing reaction speed of isophthaloyl dichloride
-
Paragraph 0019-0033, (2020/05/01)
The invention belongs to the technical field of organic synthesis, and particularly relates to a method for increasing the reaction speed of isophthaloyl dichloride. The method comprises the followingsteps: adding acetonitrile into thionyl chloride, adding a mixture of thionyl chloride and acetonitrile, isophthalic acid and a catalyst into a reaction kettle, carrying out a reflux reaction, and carrying out after-treatment after the reaction is finished, thereby obtaining isophthaloyl dichloride. Compared with a traditional thionyl chloride method, acetonitrile is added as an auxiliary catalyst, so the reaction activity of isophthalic acid is improved, reaction time is greatly shortened by 30%, and yield is increased; and the purity of the produced isophthaloyl dichloride reaches 99.92% orabove, and the yield is greater than 99%.
Synthesis, antimicrobial activity, and ion transportation investigation of four new [1 + 1] condensed furan and thiophene-based cycloheterophane amides
?zcan, Hafize,Erku?, Betül,Zaim, ?mer
, (2020/02/18)
Four new macrocyclic compounds with thiophene (L1 and L2) and furan (L3 and L4) rings were synthesized and characterized by IR, 1H NMR, 13C NMR, and Q-TOF spectral data. Macrocyclic amides (L1, L2, L3, and L4) were tested for ion transportation with Na+ and K+ ions, and also, antimicrobial activities were investigated against the Gram-negative Escherichia coli ATCC 25922, Gram-positive Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 25923, Gram-negative Listeria monocytogenes ATCC 19115, Gram-negative Salmonella typhimurium ATCC 14028, Bacillus cereus bacteria, and Candida albicans ATCC 10231 for all amides.