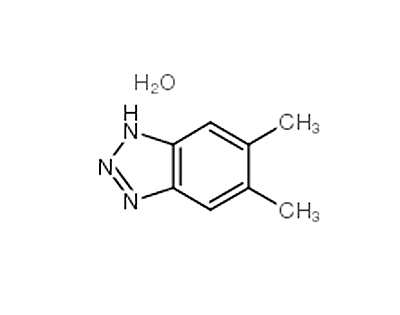
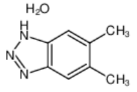
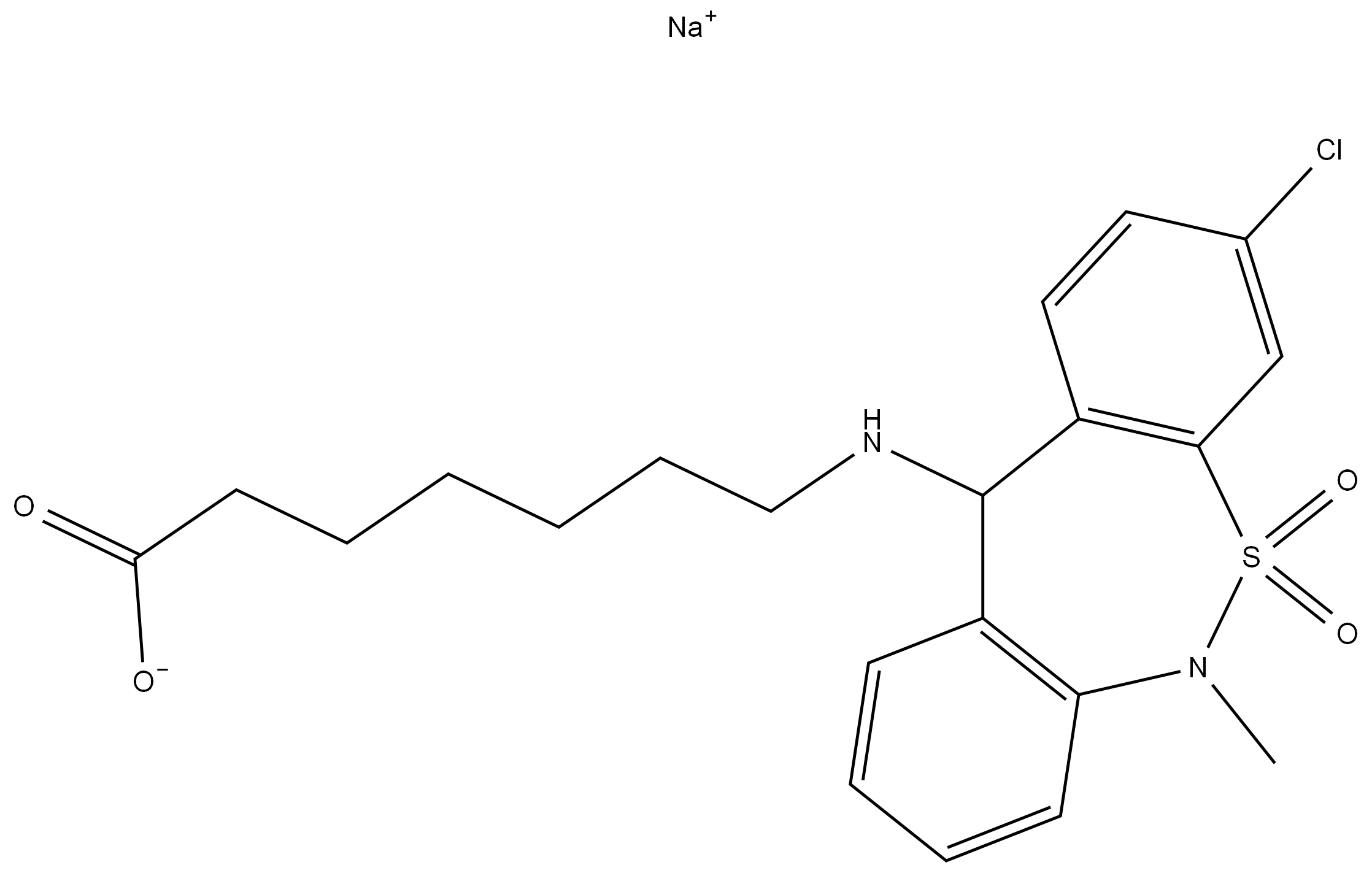
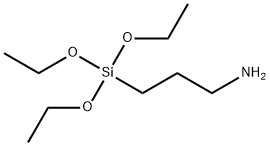
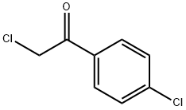
5,6-DIMETHYLAZIMIDOBENZENE literature
Selective Synthesis of N-H and N-Aryl Benzotriazoles by the [3 + 2] Annulation of Sodium Azide with Arynes
Guin, Avishek,Gaykar, Rahul N.,Bhattacharjee, Subrata,Biju, Akkattu T.
, p. 12692 - 12699 (2019/10/11)
The synthetic utility of NaN3 as the azide component in the [3 + 2] annulation with arynes generated from 2-(trimethylsilyl)aryltriflates resulting in the transition-metal-free synthesis of N-H and N-aryl benzotriazoles has been demonstrated. Using CsF as the fluoride source in CH3CN, the N-H benzotriazoles are formed in high selectivity instead of the expected azidobenzene. Interestingly, N-aryl benzotriazoles are formed using KF and THF as solvent in an open-flask reaction. Moreover, a method for the N1-arylation of benzotriazole is also presented.
Some Aspects of the Azide-Alkyne 1,3-Dipolar Cycloaddition Reaction
Pokhodylo,Tupychak,Shyyka, O. Ya.,Obushak
, p. 1310 - 1321 (2019/11/03)
Some peculiar features of two most commonly used catalytic systems (Cul and CuSOVsodium ascorbate) controlling the regioselectivity of 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition of azides to terminal alkynes have been studied. Their potentialities, main disadvantages, and limitations have been demonstrated by a number of examples, including reactions of low-molecular-weight azides and alkynes containing heterocyclic substituents. The possibility of using novel reagents in click reactions is discussed.
Synthesis of benzotriazoles derivatives and their dual potential as α-amylase and α-glucosidase inhibitors in vitro: Structure-activity relationship, molecular docking, and kinetic studies
Hameed, Shehryar,Kanwal,Seraj, Faiza,Rafique, Rafaila,Chigurupati, Sridevi,Wadood, Abdul,Rehman, Ashfaq Ur,Venugopal, Vijayan,Salar, Uzma,Taha, Muhammad,Khan, Khalid Mohammed
, (2019/09/10)
Benzotriazoles (4–6) were synthesized which were further reacted with different substituted benzoic acids and phenacyl bromides to synthesize benzotriazole derivatives (7–40). The synthetic compounds (7–40) were characterized via different spectroscopic techniques including EI-MS, HREI-MS, 1H-, and 13C NMR. These molecules were examined for their anti-hyperglycemic potential hence were evaluated for α-glucosidase and α-amylase inhibitory activities. All benzotriazoles displayed moderate to good inhibitory activity in the range of IC50 values of 2.00–5.6 and 2.04–5.72 μM against α-glucosidase and α-amylase enzymes, respectively. The synthetic compounds were divided into two categories “A” and “B”, in order to understand the structure-activity relationship. Compounds 25 (IC50 = 2.41 ± 1.31 μM), (IC50 = 2.5 ± 1.21 μM), 36 (IC50 = 2.12 ± 1.35 μM), (IC50 = 2.21 ± 1.08 μM), and 37 (IC50 = 2.00 ± 1.22 μM), (IC50 = 2.04 ± 1.4 μM) with chloro substitution/s at aryl ring were found to be most active against α-glucosidase and α-amylase enzymes. Molecular docking studies on all compounds were performed which revealed that chloro substitutions are playing a pivotal role in the binding interactions. The enzyme inhibition mode was also studied and the kinetic studies revealed that the synthetic molecules have shown competitive mode of inhibition against α-amylase and non-competitive mode of inhibition against α-glucosidase enzyme.
Tert -Butyl nitrite mediated nitrogen transfer reactions: Synthesis of benzotriazoles and azides at room temperature
Azeez, Sadaf,Chaudhary, Priyanka,Sureshbabu, Popuri,Sabiah, Shahulhameed,Kandasamy, Jeyakumar
supporting information, p. 6902 - 6907 (2018/10/02)
A conversion of o-phenylenediamines into benzotriazoles was achieved at room temperature using tert-butyl nitrite. The optimized conditions are also well suited for the transformation of sulfonyl and acyl hydrazines into corresponding azides. This protocol does not require any catalyst or acidic medium. The desired products were obtained in excellent yields in a short span of time.