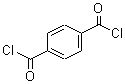
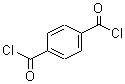
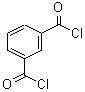
Terephthaloyl chloride literature
Incorporating Pendent Fullerenes with High Refractive Index Backbones: A Conjunction Effect Method for High Refractive Index Polymers
Chen, Shuang,Chen, Dongxue,Lu, Min,Zhang, Xin,Li, He,Zhang, Xiaoyan,Yang, Xiaoming,Li, Xiaohong,Tu, Yingfeng,Li, Christopher Y.
, p. 8480 - 8488 (2015)
To achieve high refractive index polymers (HRIPs), we report here the design and synthesis of four fullerene polyesters (P1-P4), based on the conjunction effect from the high refractive index polyester backbones and pendent fullerene side chains. At sodiu
C-I···π Halogen Bonding Driven Supramolecular Helix of Bilateral N-Amidothioureas Bearing β-Turns
Cao, Jinlian,Yan, Xiaosheng,He, Wenbin,Li, Xiaorui,Li, Zhao,Mo, Yirong,Liu, Maili,Jiang, Yun-Bao
, p. 6605 - 6610 (2017)
We report the first example of C-I···π halogen bonding driven supramolecular helix in highly dilute solution of micromolar concentration, using alanine based bilateral I-substituted N-amidothioureas that contain helical fragments, the β-turn structures. T
-
Nakano et al.
, p. 808 (1977)
-
Synthesis, thermal, and photocrosslinking studies of thermotropic liquid crystalline poly(benzylidene-ether)esters containing α,β-unsaturated ketone moiety in the main chain
Muthusamy, Athianna,Balaji, Krishnasamy,Murugavel, Salem Chandrasekaran
, p. 1707 - 1715 (2013)
A series of poly(benzylidene-ether)esters containing a photoreactive benzylidene chromophore in the main chain were synthesized from 2,6-bis(4-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzylidene)cyclohexanone (BHMBCH) with various aliphatic and aromatic diacid chlorides by an interfacial polycondensation technique. The intrinsic viscosity of the synthesized homo and copolymers determined by Ubbelohde viscometer was found to be 0.12 to 0.17 dL/g. The molecular structure of the monomer and polymers was confirmed by FT-IR, 1H NMR, and 13C NMR spectral analyses. These polymers were studied for their thermal stability and photochemical properties. Thermal properties were evaluated by thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) and differential scanning calorimetry (DSC). It was found that the polymers were stable up to 280 °C and start degrading thereafter. Increase in acid methylene spacer length decreased the thermal stability. The self-extinguishing property of the synthesized polymers was studied by calculating the limiting oxygen index (LOI) value using a Van Krevelen's equation. The influence of the length of methylene spacer on phase transition was investigated using DSC and odd-even effect has been observed. Hot-stage optical polarizing microscopic (HOPM) study showed that most of the polymers exhibited birefringence and opalescence properties. The photolysis of liquid crystalline poly(benzylidene-ether)esters revealed that α,β-unsaturated ketone moiety in the main chain dimerises through 2π + 2π cycloaddition reaction to form a cyclobutane derivative and leads to crosslinking.
Exploiting Peptidomimetics to Synthesize Compounds That Activate Ryanodine Receptor Calcium Release Channels
Robinson, Ken,Easton, Christopher J.,Dulhunty, Angela F.,Casarotto, Marco G.
, p. 1957 - 1971 (2018)
Ryanodine receptor (RyR) Ca2+-release channels are essential for contraction in skeletal and cardiac muscle and are prime targets for modification of contraction in disorders that affect either the skeletal or heart musculature. We designed and synthesized a number of compounds with structures based on a naturally occurring peptide (A peptides) that modifies the activity of RyRs. In total, 34 compounds belonging to eight different classes were prepared. The compounds were screened for their ability to enhance Ca2+ release from isolated cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) vesicles, with 25 displaying enhanced Ca2+ release. Competition studies with the parent peptides indicated that the synthetic compounds act at a competing site. The activity of the most effective of the compounds, BIT 180, was further explored using Ca2+ release from skeletal SR vesicles and contraction in intact skeletal muscle fibers. The compounds did not alter tension in intact fibers, indicating that (as expected) they are not membrane permeable, but importantly, that they are not toxic to the intact cells. Proof in principal that the compounds would be effective in intact muscle fibers if rendered membrane permeable was obtained with a structurally related membrane-permeable scorpion toxin (imperatoxin A), which was found to enhance contraction.
Infrared and Raman spectra of terephthalonitrile and terephthalonitrile-15N2. Force field for out-of-plane vibrations
Arenas, J. F.,Marcos, J. I.,Ramirez, F. J.
, p. 1045 - 1052 (1988)
A general assignment of the vibrational spectra of terephthalonitrile and terephthalonitrile-15N2 is proposed on the basis of their infrared and Raman spectra.The relevant symmetry is found to be D2h.The force field for the out-of-plane vibrati
-
Rabjohn
, p. 5479,5481 (1954)
-
Phosphazenium chloride catalysts immobilized on SBA-15 mesoporous material and silica gel: New exceptionally active catalysts for the chlorination of organic acids
Kim, Keun-Sik,Kim, Jong-Ho,Seo, Gon
, p. 372 - 373 (2003)
Novel reusable phosphazenium chloride catalysts immobilized on SBA-15 mesoporous material and silica gel show exceptional activities and selectivities even in the continuous chlorination reaction of organic acids with thionyl chloride or phosgene.
Effect of regioisomerism on the self-assembly and photophysical behavior of 1,3,4-thiadiazole-based polycatenars
Pathak, Suraj Kumar,Nath, Subrata,Gupta, Ravindra Kumar,Rao, D. S. Shankar,Prasad, S. Krishna,Achalkumar, Ammathnadu S.
, p. 8166 - 8182 (2015)
A new class of polycatenars, where the central benzene ring is connected to two arms derived from substituted 1,3,4-thiadiazoles at the 1,3- and 1,4-positions, was synthesized and characterized. These thiadiazole-based molecules are promising as they stabilize columnar phases over a wide temperature range, in comparison to their oxadiazole analogues. The para-substituted polycatenars exhibited a columnar hexagonal and/or a columnar oblique phase, while the meta-substituted polycatenars exhibited solely a columnar oblique phase. The para-substituted polycatenars exhibited green emission, while the meta-substituted polycatenars exhibited blue emission in solution and film states. Stabilization of a broad range columnar phase and luminescence in the solid state make these new compounds promising from the viewpoint of applications in emissive displays. The self-assembly and luminescence of these regioisomers was greatly influenced by the molecular structure.
Aromatic Esters, Carbinols, and Derivatives Thereof with Perfluorohexyl Residues as Alternatives to Perfluoroalkanecarboxylic and -sulfonic Acids
Alpers, Torben,Muesmann, Thomas W. T.,Temme, Oliver,Christoffers, Jens
, p. 609 - 617 (2017)
Four perfluorohexyl carbinols have been prepared from the corresponding Grignard reagent and benzaldehyde, terephthalaldehyde, isophthalaldehyde, and trimesaldehyde. The corresponding secondary alcohols were then transformed by alkylation and acylation reactions to form a total of 14 ethers (methyl, ethyl, propyl, and n-hexyl ethers) and esters (acetyl and 2-ethylhexanoyl), respectively. Furthermore, 11 perfluoroalkyl carboxylates were prepared from aromatic, heteroaromatic, and aliphatic mono-, di-, tri-, and tetracarboxylic acids and tridecafluorooctanol. The wettability of all 29 materials was investigated by the water contact angle measurements of thin films on glass surfaces. In up to six cases, contact angles greater than 130° were observed, which indicates that the products might be suitable candidates for the impregnation of surfaces. With their relatively short perfluoroalkyl side-chains and therefore low bioaccumulativity, the target compounds might be beneficial alternatives to established products.
Photo-on-Demand Synthesis of Vilsmeier Reagents with Chloroform and Their Applications to One-Pot Organic Syntheses
Liang, Fengying,Eda, Kazuo,Okazoe, Takashi,Wada, Akihiro,Mori, Nobuaki,Konishi, Katsuhiko,Tsuda, Akihiko
, p. 6504 - 6517 (2021)
The Vilsmeier reagent (VR), first reported a century ago, is a versatile reagent in a variety of organic reactions. It is used extensively in formylation reactions. However, the synthesis of VR generally requires highly toxic and corrosive reagents such as POCl3, SOCl2, or COCl2. In this study, we found that VR is readily obtained from a CHCl3 solution containing N,N-dimethylformamide or N,N-dimethylacetamide upon photo-irradiation under O2 bubbling. The corresponding Vilsmeier reagents were obtained in high yields with the generation of gaseous HCl and CO2 as byproducts to allow their isolations as crystalline solid products amenable to analysis by X-ray crystallography. With the advantage of using CHCl3, which bifunctionally serves as a reactant and a solvent, this photo-on-demand VR synthesis is available for one-pot syntheses of aldehydes, acid chlorides, formates, ketones, esters, and amides.
Synthesis of poly β ketoesters via double acylketene trapping
Palma, Aniello,Serginson, James M.,Barrett, Anthony G.M.
, p. 674 - 676 (2015)
The synthesis and characterization of polymeric β ketoesters is herein reported. These polymers were prepared by allowing highly electrophilic acylketenes, generated in situ via thermolysis of stable 6-substituted-2,2-dimethyl-4H-1,3-dioxin-4-ones, to rea
Synthesis and characteriation of novel poly (ester amide)s containing benzthiazole heterocyclic ring
Patel,Desai,Patel
, p. 203 - 208 (2004)
The novel Poly (ester-amide)s (PEAs) were prepared by inrter-facial polycondensation of 5 - hydroxy - 2 - amino benzthiazole with various di-basic acid chlorides. The PEAs were characterized by elements analysis, IR spectra studies, Mn estimated by non aqueous conductometric titration and thermogravimetry. The electric conductivity of all the poly (ester amide)s PEAs was also measured at room temperature and it was found that the PEAs have semiconducting properties.
Primary coloured electrochromism of aromatic oxygen and sulfur diesters
Xu, Xiuhui,Webster, Richard D.
, p. 18100 - 18107 (2014)
Eleven aromatic diesters and thioic S,S′-diesters were synthesized and investigated using electrochemical (cyclic voltammetry and controlled potential electrolysis) and UV-vis spectroscopic techniques over a range of temperatures. Nine of the compounds exhibited vibrant colour changes from a colourless state in their neutral forms to brightly coloured upon one-electron electrochemical reduction in acetonitrile. The compounds were found to display either red, green or blue colours in their one-electron reduced states. The electrochromic properties of 3 of the compounds that displayed the most vibrant colour changes were examined in solution using a gold micro-mesh electrode laminated inside a polymer film.
Structure-activity relationships of analogues of NF449 confirm NF449 as the most potent and selective known P2X1 receptor antagonist
Kassack, Matthias U.,Braun, Kirsten,Ganso, Matthias,Ullmann, Heiko,Nickel, Peter,Boeing, Barbara,Mueller, Gregor,Lambrecht, Guenter
, p. 345 - 357 (2004)
NF449 [4,4′,4″,4′′′-(carbonylbis(imino-5,1,3- benzenetriyl-bis(carbonylimino)))tetrakisbenzene-1,3-disulfonic acid-octasodiumsalt)] was recently described to inhibit recombinant rP2X 1 receptors (Naunyn Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 364 (2001
Novel bivalent securinine mimetics as topoisomerase I inhibitors
Hou, Wen,Lin, Hui,Wang, Zhen-Ya,Banwell, Martin G.,Zeng, Ting,Sun, Ping-Hua,Lin, Jing,Chen, Wei-Min
, p. 320 - 328 (2017)
A series of novel bivalent securinine mimetics incorporating different linkers between C-15 and C-15′ were synthesized and their topoisomerase I (Topo I) inhibitory activities evaluated. It was thus revealed that mimetic R2 incorporating a rigid m-substituted benzene linker exhibits Topo I inhibitory activity three times that of parent securinine. Comprehensive structure-activity relationship analyses in combination with docking studies were used to rationalize the potent activity of these bivalent mimetics. Mechanistic studies served to confirm the deductions arising from docking studies that the active bivalent mimetics not only inhibited complexation between Topo I and DNA but also stabilized the Topo I-DNA complex itself.
Photolysis of p-Phenylbis(chlorodiazirine), Studied by Matrix Isolation Spectroscopy. Generation, Detection and Characterization of p-Phenylenebis(chloromethylene)
Tomioka, Hideo,Komatsu, Kazunori,Nakayama, Takehito,Shimizu, Masayoshi
, p. 1291 - 1294 (1993)
Photolysis of the title bis-diazirine matrix-isolated in Ar at 10 K monitored by IR and UV/vis spectroscopy indicated that the diazirine underwent stepwise elimination of N2 to produce 3-(4-chlorocarbenophenyl)-3-chlorodiazirine which then eliminated the
Br?nsted acid-catalyzed chlorination of aromatic carboxylic acids
Yu, Zhiqun,Yao, Hongmiao,Xu, Qilin,Liu, Jiming,Le, Xingmao,Ren, Minna
supporting information, p. 685 - 689 (2021/04/09)
The chlorination of aromatic carboxylic acids with SOCl2 has been effectively performed by reacting with a Br?nsted acid as the catalyst. Based on this discovery, an efficient catalytic method that is cheaper than traditional catalytic methods was developed. 20 substrates were chlorinated offering excellent yields in a short reaction time. And the SOCl2/Br?nsted acid system has been used in a larger scale preparative reaction. A dual activation mechanism was proposed to prove the irreplaceable system of SOCl2/Br?nsted acid.
Preparation method of terephthaloyl chloride
-
Paragraph 0028; 0030-0041, (2021/10/27)
The invention discloses a preparation method of terephthaloyl chloride, and belongs to the technical field of organic chemical synthesis. To 85 - 110 °C reaction 5 - 10h, after the reaction is finished, the reaction mixture is separated from the catalyst,
BENZENE 1,4-BIS(BISPHOSPHONIC ACID)-BASED METAL COMPLEXES, METHOD OF SYNTHESIS AND APPLICATIONS THEREOF
-
Paragraph 0103; 0104, (2021/10/15)
The invention provides extended bisphosphonate-based metal complexes using benzene1,4-bis(bisphosphonic acid) (BBPA), an analog of benzene 1,4-dicarboxylic acid (BDC). Hydrothermal synthesis of BBPA with the bioactive metals Ca2+, Zn2+