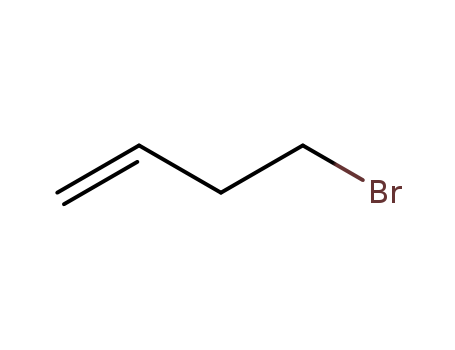
4-Bromo-1-butene literature
Formal Bromine Atom Transfer Radical Addition of Nonactivated Bromoalkanes Using Photoredox Gold Catalysis
Zidan, Montserrat,McCallum, Terry,Swann, Rowan,Barriault, Louis
supporting information, p. 8401 - 8406 (2020/11/03)
Organic transformations mediated by photoredox catalysis have been at the forefront of reaction discovery. Recently, it has been demonstrated that binuclear Au(I) bisphosphine complexes, such as [Au2(μ-dppm)2]X2, are capable of mediating electron transfer to nonactivated bromoalkanes for the generation of a variety of alkyl radicals. The transfer reactions of bromine, derived from nonactivated bromoalkanes, are largely unknown. Therefore, we propose that unique metal-based mechanistic pathways are at play, as this binuclear gold catalyst has been known to produce Au(III) Lewis acid intermediates. The scope and proposed mechanistic overview for the formal bromine atom transfer reaction of nonactivated bromoalkanes mediated by photoredox Au(I) catalysis is presented. The methodology presented afforded good yields and a broad scope which include examples using bromoalkanes and iodoarenes.
Simple and high yield access to octafunctional azido, amine and urea group bearing cubic spherosilicates
Sch?fer, Sandra,Kickelbick, Guido
supporting information, p. 221 - 226 (2016/12/28)
Spherosilicates and polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxanes represent unique well-defined rigid building blocks for molecular and hybrid materials. Drawbacks in their synthesis are often low yields and the restricted presence of functional groups either based on incomplete transformation of all corners or the reactivity of the functional groups. Particularly amine-functionalization reveals some synthetic challenges. In this study we report the synthesis of a new class of octafunctionalized hydrogen bond forming spherosilicates via a facile route based on octabromo alkyl functionalized cubic spherosilicates. Four different alkyl chain lengths, namely C4, C5, C6 and C11, were realized starting from ω-alkenylbromides via hydrosilylation of Q8M8H. Using sodium azide in a mixture of acetonitrile:DMF = 10:1, the octaazide was obtained quantitatively and could be rapidly transformed in an octaamine cube via catalytic hydrogenation over Pd/C in absolute ethanol. The following reaction to hydrogen bond forming spherosilicates was performed in situ by adding propyl isocyanate. All transformations proceed quantitatively at the eight corners of the cube, which was evidenced by NMR spectroscopy and ESI-MS measurements. The Q8-target compound can be separated after each reaction step over simple chemical workup while no cage rearrangement was observed. The structures were confirmed using 1H, 13C, 29Si-NMR, FT-IR, elemental analysis and ESI-MS. The method opens a high yield route (overall isolated yield 83-88%) for structural building blocks in hybrid materials.
Asymmetric Synthesis of Carbocyclic Propellanes
Schneider, Lisa M.,Schmiedel, Volker M.,Pecchioli, Tommaso,Lentz, Dieter,Merten, Christian,Christmann, Mathias
supporting information, p. 2310 - 2313 (2017/05/12)
A modular synthesis of functionalized carbocyclic propellanes was developed. Formation of the first of two quaternary bridgehead centers has been achieved by desymmetrization of prostereogenic ketones by either Hajos-Parrish-Eder-Sauer-Wiechert-type processes or Werner’s catalytic asymmetric Wittig reaction. The obtained bicyclic enones were subjected to conjugate additions upon which the remaining ring was formed by olefin metathesis. All bridges are amenable to further derivatization, which renders those compounds useful as central units in fragment-based drug discovery or as ligand scaffolds.
Structural and Electronic Noninnocence of α-Diimine Ligands on Niobium for Reductive C-Cl Bond Activation and Catalytic Radical Addition Reactions
Nishiyama, Haruka,Ikeda, Hideaki,Saito, Teruhiko,Kriegel, Benjamin,Tsurugi, Hayato,Arnold, John,Mashima, Kazushi
, p. 6494 - 6505 (2017/09/12)
A d0 niobium(V) complex, NbCl3(α-diimine) (1a), supported by a dianionic redox-active N,N′-bis(2,6-diisopropylphenyl)-1,4-diaza-2,3-dimethyl-1,3-butadiene (α-diimine) ligand (ene-diamido ligand) served as a catalyst for radical addition reactions of CCl4 to α-olefins and cyclic alkenes, selectively affording 1:1 radical addition products in a regioselective manner. During the catalytic reaction, the α-diimine ligand smoothly released and stored an electron to control the oxidation state of the niobium center by changing between an η4-(σ2,π) coordination mode with a folded MN2C2 metallacycle and a κ2-(N,N′) coordination mode with a planar MN2C2 metallacycle. Kinetic studies of the catalytic reaction elucidated the reaction order in the catalytic cycle: the radical addition reaction rate obeyed first-order kinetics that were dependent on the concentrations of the catalyst, styrene, and CCl4, while a saturation effect was observed at a high CCl4 concentration. In the presence of excess amounts of styrene, styrene coordinated in an η2-olefinic manner to the niobium center to decrease the reaction rate. No observation of oligomers or polymers of styrene and high stereoselectivity for the radical addition reaction of CCl4 to cyclopentene suggested that the C-C bond formation proceeded inside the coordination sphere of niobium, which was in good accordance with the negative entropy value of the radical addition reaction. Furthermore, reaction of 1a with (bromomethyl)cyclopropane confirmed that both the C-Br bond activation and formation proceeded on the α-diimine-coordinated niobium center during transformation of the cyclopropylmethyl radical to a homoallyl radical. With regard to the reaction mechanism, we detected and isolated NbCl4(α-diimine) (6a) as a transient one-electron oxidized species of 1a during reductive cleavage of the C-X bonds; in addition, the monoanionic α-diimine ligand of 6a adopted a monoanionic canonical form with selective one-electron oxidation of the dianionic ene-diamido form of the ligand in 1a.